If you’re in the healthcare industry, this won’t be the first time you’ve heard about HIPAA.
It’s a mandatory US legislation for healthcare organizations, and if you run a clinic, you’re legally obliged to comply with its regulations under federal law.
This is because you’re handling confidential medical information about your patients, known as PHI (protected health information) – anything from their name, phone number and email address to physician’s notes and lab test results.

Even if it doesn’t come to that, the reputational damage is huge — being able to repair the loss of trust from clients would be very difficult, if not impossible.
To play your cards right, you need robust software to support you in staying HIPAA compliant, to supplement the procedures and policies you need to implement in-house.
This guide will help you navigate the software requirements for HIPAA compliance.

Understanding HIPAA compliance
HIPAA, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, is a law designed to protect sensitive patient information. With that in mind, healthcare practitioners must know this law’s key goals and objectives to ensure they comply with it.
Clinics must choose software that helps them comply with HIPAA compliance requirements. The kind of software you’d need would have features that:
✅Protect patient health information (PHI) such as names, telephone numbers, geographic data, social security numbers, medical health record numbers, etc
✅Provide secure access to patient data with data encryption features to make sure patient data is securely transmitted and stored without the risk of unauthorized access
✅Protect against data loss with regular data backups to ensure that PHI is preserved and can be restored in case of a system failure, natural disaster, or other incidents
5 HIPAA rules medical software must adhere to
The brains behind HIPAA, the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), created five rules to improve the overall quality of healthcare delivery.
All of them are essential in ensuring that patient data is handled securely and responsibly, leading to better patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Security rule 🔒
The HIPAA security rule took full effect in 2005 when digital record keeping became popular, and there was a need to document how electronic records were collected, shared, and stored.
For your software to be compliant with HIPAA’s security rule, it must address three key standards:
- Administrative safeguards: Conduct regular risk assessments to identify ePHI breaches, implement a risk management policy and emergency plan, HIPAA training for employees, and restrict third-party access to ePHI
- Physical safeguards: Give authorized access to your PHI only to those who need it, create strong passwords to all devices with ePHI, and set workstations to log off or switch to screensavers every 5 minutes or so
- Technical safeguards: Check who has access controls to your patient health information and limit it only to those who need it
2. Privacy rule 👁️🗨️
The HIPAA privacy rule focuses on how your clinic should protect and maintain the confidentiality of PHI and to whom it gives access. It ensures that only authorized personnel, such as a practitioner or a medical director, can access it.
Also, this rule is governed by how patients are notified about their information being shared. It also means that healthcare providers must obtain patient consent before they disclose any of their PHI.
You need software with built-in features that provide:
- Customizable staff and patient permissions: To grant and revoke access only to those that are in need of such information
- Patient photos data security: If your clinic uses patient images, ensuring those are stored in a safe place is crucial. Patient images are also part of a patient’s medical record, so safeguarding them is critical.
- Consent before disclosing PHI: The privacy rule requires healthcare providers to obtain patient consent before sharing PHI. This approach promotes respect for patient privacy while securing their medical data within your clinic.
3. Enforcement rule 👮
HIPAA enforcement is enforced by the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) and exists to investigate and penalize clinics if they don’t comply with HIPAA regulations.
Not to give you the chills or anything, but fines for violating the HIPAA enforcement rule are pretty steep – they can go up to $1,500,000 (depending on the type of violation). Generally, HIPAA violations are due to:
- Lack of knowledge: You or one of your team members were unaware that you were making a HIPAA violation (for example, by inadvertently posting identifiable PHI on social media or by even replying to reviews)
- Negligence: You can correct a violation within 30 days. Otherwise, you must pay a fine (for example, failing to report PHI breaches or not providing notice of privacy practices)
4. Breach notification rule ⚠️
HIPAA’s breach notification rule ensures patients are notified when their personal health information leaks out.
With this rule, clinics must report any security incidents that could compromise the security of patients’ unprotected health data. For example, if there is a PHI breach on social media by HIPAA, you’ll be required to investigate and mitigate the risks associated with that data breach.
Let’s not forget that you must also keep solid documentation of your actions to address the breach issue. This shows that you’re not just focused on protecting patient data but also committed to ensuring their well-being and safety.
5. Omnibus rule📜
Implemented in 2013, the omnibus rule is an extension of the HIPAA regulations to protect patient health information.
In a nutshell, it applies to the clinic’s business associates so they can take the necessary measures to protect PHI (patient health information).
💡Good to know: If an international company handles the patient health information of US citizens, it counts as a business associate of a covered entity and must follow HIPAA rules.
As the Omnibus rule is the more recent rule released by HIPAA, its purpose is to harmonize all previously passed regulations and strengthen patient privacy and PHI specifically in the digital world.
Let’s say you are using an Electronic Health Record (EHR) system that is integrated into your software, for example. To comply with this HIPAA rule, your software must ensure that all of that data is
- Encrypted: A software that uses strong encryption protocols to protect patient data both when it’s stored in the system and when it’s being transmitted.
- Cannot be accessed or modified by unauthorized personnel: It needs to have strong some form of access privilege functionality to avoid this.
- Accessible to patients: Patients can access their health records, request changes, and specify who can view their information.
Key features for software to be HIPAA complaint
Software with built-in features that help you comply with HIPAA can help you sleep better at night, as it provides all of these functionalities in one place.
Data encryption 🛡️
You need software with industry-standard encryption protocols to protect your patient data and safely store it within the system.
This ensures that sensitive information, such as patient’s medical records, contact details, appointment histories, and lots more, is safely transported and stored in an encrypted format.
With a robust software system that uses end-to-end encryption techniques, you can reduce the risk of unauthorized access and keep your patient data safe and secure.
Access controls🔑
Access control features in HIPAA-compliant software are paramount.
Robust software allows you to assign role-based access privileges so that only authorized personnel can view confidential patient records.
For example, say you have a patient, and you want only one doctor to have access to their medical records. You can set up the system so that only they can view their files.
Additionally, look for software that has:
- Strong password policies: Software that alerts you if your password is too weak and prompts you to create a stronger, more complex one.
- Multi-factor user authentication: When users try to log in to your software, they’ll need to take additional login steps, such as having a code sent to their personal device, to make sure it’s them.
- Session timeouts: For example, one that automatically logs you out of the system if you’ve not moved the mouse in 10 minutes or so.
Audit logs and monitoring 📈
Audit logs are important because they document every activity within your software system used across your clinic. They can track your staff to see who accessed specific healthcare data, their actions, and the information they viewed.
With audit controls, you can easily identify potential security breaches or unauthorized access attempts. For example, if an unauthorized user tries to access your PHI, you can create an audit trail, monitor the situation, and see the device or object that was impacted, as well as the IP address, device ID, and so on.
Secure communication channels💬
Secure communication channels are also a requirement of HIPAA.
HIPAA wants to ensure that every piece of information that goes from one channel to another is safe and secure.
- Whenever you send emails and SMS messages (internally, among staff members, or externally, to clients – information like their diagnosis, treatment plans, or surgical procedures must be secured with end-to-end encryption
- Patient portals: Since patient portals facilitate direct interaction between patients and their healthcare providers, these communication channels must also be secured through encryption, access controls, or authentication
- Telehealth functionalities: If you provide video conferencing, to be HIPAA compliant, you must also ensure the communication that takes place through the video conference is also secured through data encryption
Physical security measures🚨
Physical security measures are also necessary to avoid HIPAA non-compliance.
Look for software with a HIPAA compliance feature you can enable/disable on your account. With a single click, you can enable physical security measures and impose restrictions on sharing information via SMS and email from your client record’s EMR and financial sections.
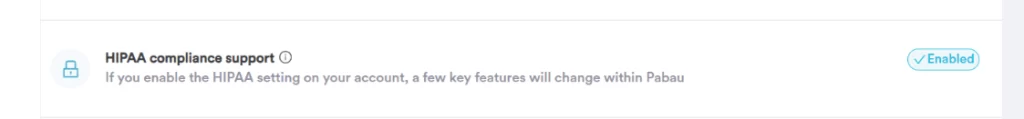
A feature like this makes it easy for you to comply with HIPAA’s safeguards by
- Facility access controls: Set user permissions to grant only those that are logged into the system to have access to sensitive patient health information
- Workstation use: Your staff must be informed about the procedures for using/accessing data (where, how, and when to access it)
- Device controls: Set strong password protection policies, passwords that expire every 90 days, limit invalid login attempts, enforce password history, and implement a lockout period of five or 10 minutes
Backup and disaster recovery 💾
Regular backup and cloud storage for clinics are not nice-to-have – they really are a must! We all saw what happened when a Microsoft software update went wrong recently – it caused havoc at airports, private practices, and much more.
Make sure you look for software that protects against data loss and provides robust disaster recovery procedures.
In other words, it must offer measures to ensure your patient information is always preserved and can be restored in situations like system failure, natural disasters, or other incidents you cannot predict.
Experience easy HIPAA compliance management with Pabau👌
Just to be clear – there is no magic bullet that will instantly make you HIPAA compliant. It’s a little more complex than that, unfortunately.
You’ll have to do the work on the ground level and implement policies and procedures to comply with HIPAA. However, software like Pabau are there to support you and help your clinic stay HIPAA compliant.
Pabau is an all-in-one practice management solution with built-in functionalities that will help you manage complex medical information safely and securely.
Here’s a quick taster:
- Role-based permissions settings so that only authorized medical personnel can access client records
- End-to-end encryption to ensure secure secure communication and prevent third parties from accessing data when it’s transferred
- Regular backup and cloud storage to preserve PHI so it can be restored in situations like system failure, natural disasters, or other incidents
- Strict access controls with strong password policies, multi-factor authentication, and session timeouts
Take the leap and learn how Pabau helps with HIPPA compliance – starting today.